Hong Kong Green Capabilities in Real Estate Development and Property Management: RCEP Opportunities
This assessment report of Hong Kong's green capabilities in the real estate development and property management sector and opportunities for future Hong Kong‑ Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) collaboration provides an understanding how Hong Kong practitioners can work closer with their RCEP counterparts to build a more green and sustainable future. The subsequent findings from both qualitative and quantitative research show how Hong Kong's green building competencies may be optimised to pitch to RCEP – the world's largest free trade bloc.
Hong Kong's Green Building Capabilities
Energy saving and green buildings take centre stage as one of the four major decarbonisation strategies in Hong Kong’s Climate Action Plan 2050. Encouraging progress has been seen across the city regarding green building development, thanks particularly to the significant efforts made by different industry stakeholders along the whole value chain. More solutions and synergies are becoming available to enable stakeholders to accelerate their contribution to the city’s decarbonisation masterplan with the ultimate goal of reaching net zero carbon emissions targets by 2050.
Key findings on the city's green building development and capabilities from in‑depth interviews with local industry practitioners are highlighted as follows:
Green finance: Hong Kong is Asia’s leading green finance hub and an active arranger and user of different green finance products, with a deep capital pool and the knowledge and experience to structure securities to meet different financing needs of the real estate sector.
Green building products and embodied carbon reduction: Local manufacturers of construction materials have made use of waste materials in their production processes to reduce embodied carbon emissions.
Industry coherence: Hong Kong’s well‑established testing, inspection, and certification industry plays a pivotal role in certifying both green building products and projects, while facilitating transfer of knowhow across the industry. The homegrown BEAM Plus Assessment Tool (previously known as HK‑BEAM) is one of the world’s first green building standards.
Innovative construction methods: The application of new construction approaches with higher efficiency and lower production costs like digitalisation and prefabrication has been widely pioneered by private sector real estate developers in Hong Kong. Their formal inclusion into the city’s General Specification for Building has created significant positive impact on the industry.
Facility management: Hong Kong is world‑renowned for its skyline of supertall skyscrapers and is therefore turning up the dial on high‑rise sustainable development and management. HVAC is a major source of energy consumption of buildings, and facility managers worldwide are looking for new ways to upgrade hardware and monitor efficiency. Retro‑commissioning and retrofitting have become common practices in Hong Kong, helping project owners and facility managers improve their sustainability performance through effective stakeholder engagement.
Alternative and renewable energy and sustainable lifestyle: Hong Kong’s adoption of alternative and renewable energy sources is more advanced than most, if not all, RCEP members. The city’s power suppliers have also been promoting sustainable lifestyle and energy efficiency through measures like renewable energy development, energy management, digitalisation and retrofitting.
Sustainable community development: Hong Kong’s industry practitioners have taken sustainable development beyond traditional frameworks through promoting low carbon lifestyles and inclusive community building. Stakeholder engagement considers the needs and wants of all stakeholders, building features such as common social facilities and shared climate‑resilient infrastructure into the design of real estate developments to create sustainable, well‑connected communities.
RCEP's Market Overview
Environmental and social factors are key drivers
Our quantitative survey results show that green building activities in the five selected RCEP markets are mainly driven by environmental concerns, followed by social considerations. Reducing energy consumption, encouraging sustainable business practices and lowering greenhouse gas emissions are the top three reasons for green building practices, chosen by 43%, 41% and 35% of respondents respectively. In terms of specific green building approaches, site planning and construction management (85%) is ranked top, followed by sustainable‑related architectural design and construction techniques (83%), and energy and waste management (81%).
Challenges vary from market to market
While sustainability has gone mainstream, challenges for green building activities vary across countries. Japan, South Korea and Singapore face high initial costs, with 46%‑56% of respondents claiming costs as the top challenge for increasing green building activities. Mainland China suffers from a lack of experienced talent (44%), while Japan is struggling with securing financial resources (40%). The poor availability of certified green building products and services is another area of concern among the South Korean (32%) and mainland Chinese (33%) respondents.
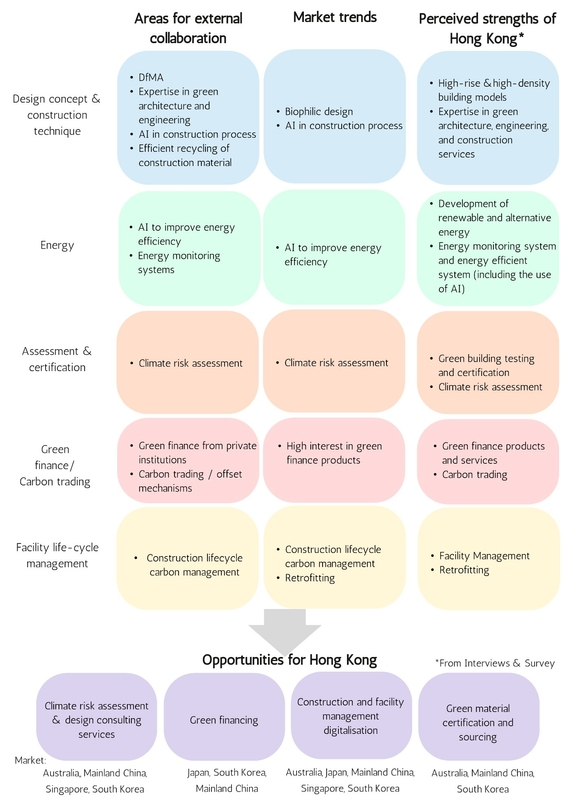
Opportunities for Hong Kong
Survey respondents see weaknesses in such areas as construction materials recycling, carbon trading mechanisms, climate risk assessment and the use of design for manufacture and assembly (DfMA), while biophilic design, the adoption of AI to improve energy efficiency and construction processes, construction lifecycle carbon management and climate risk assessment are expected to become more important going forward. Respondents recognise Hong Kong’s status as a high‑rise, high‑density cosmopolitan city with one of the world’s most service‑oriented economies, a well‑established testing, inspection and certification (TIC) industry and a first‑rate international financial hub.
The views of the survey respondents together with the in‑depth stakeholder interviews carried out in Hong Kong and the five selected RCEP markets suggest four major areas where Hong Kong’s green building capabilities can best meet the needs of RCEP markets. They are:
- Climate risk assessment and design consulting services in Australia, mainland China, Singapore and South Korea;
- Green financing, particularly in Japan, mainland China and South Korea;
- Construction and facility management digitalisation across the 5 selected RCEP markets Australia, Japan, mainland China, Singapore and South Korea; and
- Green building products certification and sourcing in Australia, mainland China and South Korea.






















































First, please LoginComment After ~