Developing Asia's 2023 Growth Outlook Upgraded to 4.9%
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has raised its economic forecast for developing economies in Asia and the Pacific, after robust domestic demand drove higher-than-expected growth in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and India.
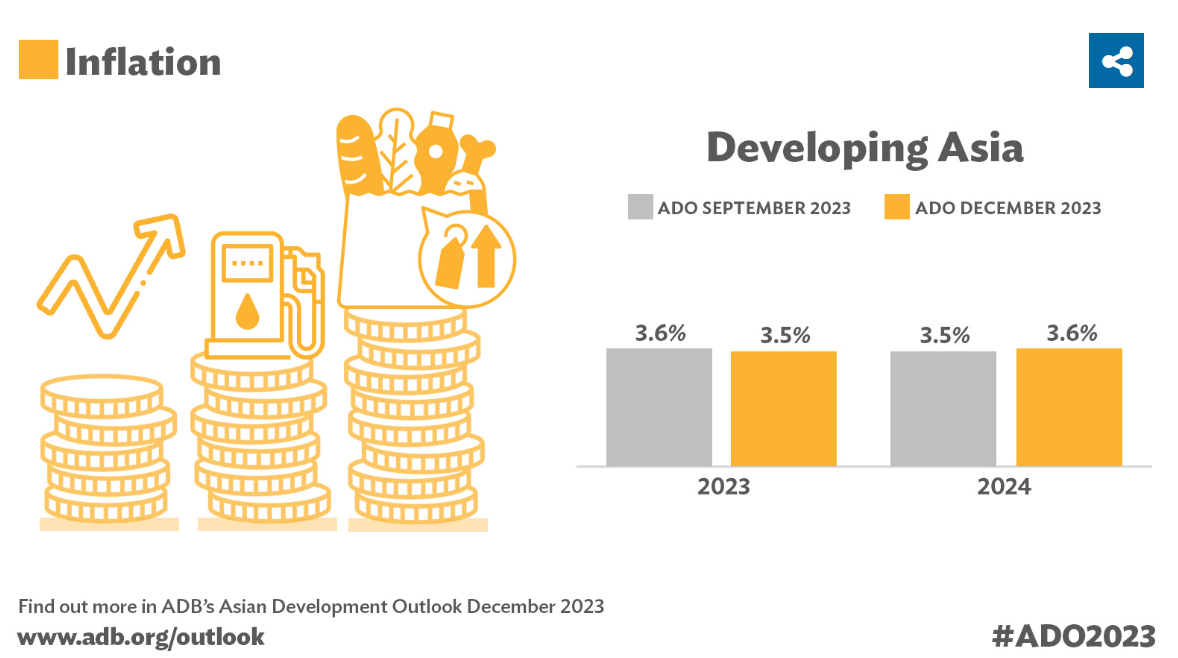
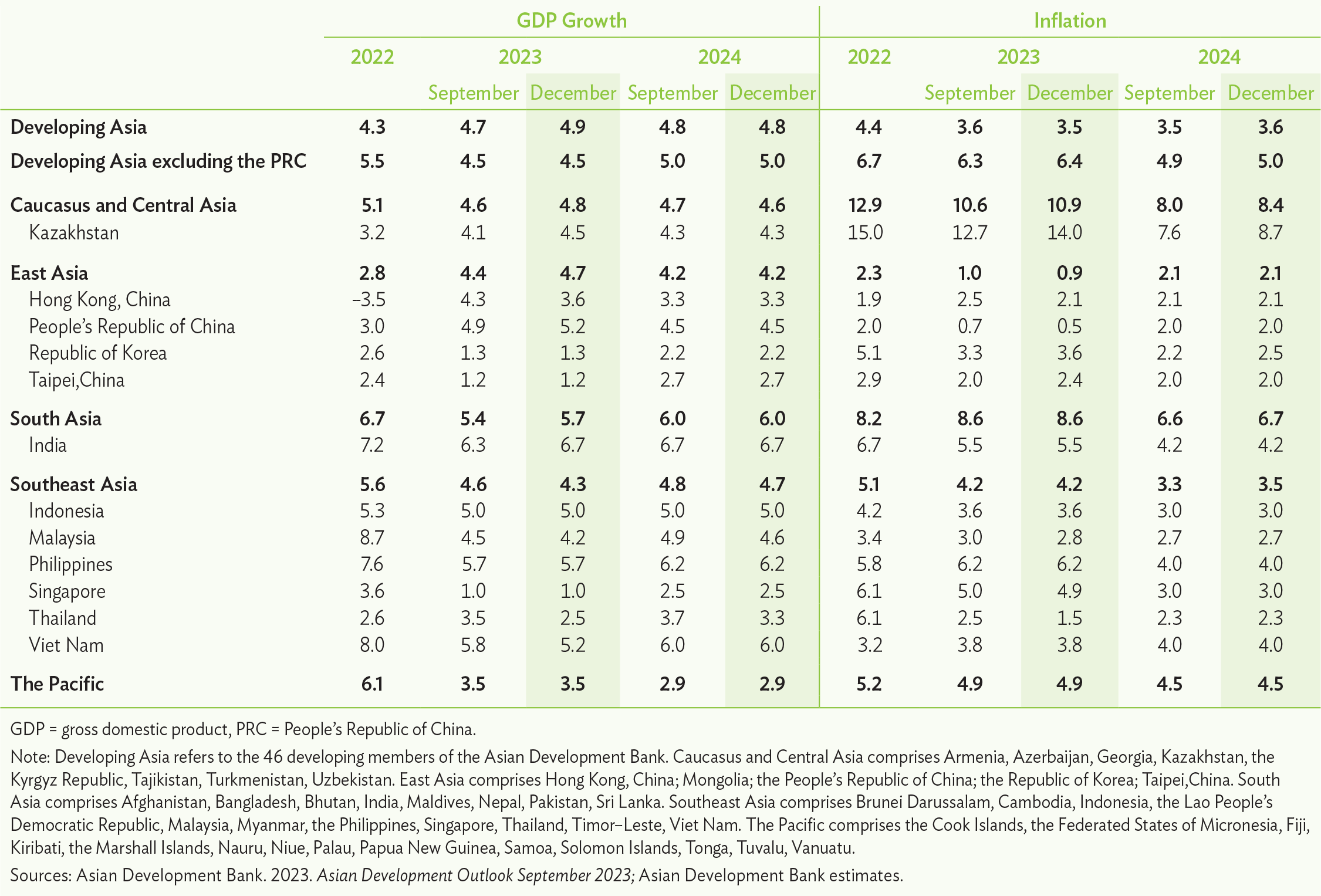
The regional economy is expected to grow 4.9% this year, compared with a previous forecast of 4.7% in September, according to the Asian Development Outlook (ADO) December 2023, released today. The outlook for next year is maintained at 4.8%.
The PRC’s economy is projected to expand by 5.2% this year, compared with a previous forecast of 4.9%, after household consumption and public investment boosted growth in the third quarter. The growth outlook for India has been raised to 6.7% from 6.3% following faster-than-expected expansion in July-September, driven by double-digit growth in industry. The upgrades for the PRC and India more than offset a lowering of the forecast for Southeast Asia, caused by lackluster performance in the manufacturing sector.
“Developing Asia continues to grow at a robust pace, despite a challenging global environment,” said ADB Chief Economist Albert Park. “Inflation in the region is also gradually coming under control. Still, risks remain, from elevated global interest rates to climate events such as El Niño. Governments in Asia and the Pacific need to remain vigilant to ensure that their economies are resilient, and that growth is sustainable.”
The region’s inflation outlook for this year has been lowered to 3.5% from an earlier projection of 3.6%, according to ADO December 2023. For next year, inflation is expected to edge up to 3.6%, compared with a previous forecast of 3.5%.
The growth outlook for Southeast Asia this year has been lowered to 4.3% from 4.6%, amid weak demand for manufacturing exports. The outlook for economies in the Caucasus and Central Asia has been raised slightly, while projections for Pacific economies are unchanged.
Risks to the outlook include persistently elevated interest rates in the United States and other advanced economies, which could contribute to financial instability in vulnerable economies in the region, especially those with high debt. Potential supply disruptions caused by the El Niño weather pattern or the Russian invasion of Ukraine could also rekindle inflation, particularly regarding food and energy.
ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty. Established in 1966, it is owned by 68 members—49 from the region.





















































First, please LoginComment After ~